HAIR LOSS STATISTICS FOR MEN
According to the American Health Journal, there are approximately 40 million men in United States suffering some degree of baldness. This may range from diffuse thinning to demoralizing baldness. Ninety-five percent of baldness in men is androgenic alopecia, or pattern baldness. By the age of 35, two-thirds of men will suffer male pattern baldness and by the age of 50, this percentage will rise to 85%. For 25% of all of these, hair loss began before the age of 21.
HAIR LOSS STATISTICS FOR WOMEN
The American Health Journal also tells us that a shocking 21 million U.S. women suffer from baldness. Some experience extensive loss while others notice that their hair is not as thick as it used to be. As with men, the leading cause of this condition is pattern baldness, though it manifests differently in women. In addition, women are more likely to experience outlying causes of hair loss, possibly from psychological illness or environmental variables. Ultimately, fifty percent of women over the age of 40 will have some degree of hair loss.
ADDITIONAL CAUSES
A variety of causes are more often seen in women than in men. Some are temporary and some permanent, to include:
Temporary Hair Loss
- Severe stress
- Sleep deprivation
- Pregnancy
- Drug use
- Illness
- Malnourishment
- Iron/folic acid deficiency
- Poor circulation
- Hormone imbalance
- Untreated hypothyroidism
- Telogen effluvium
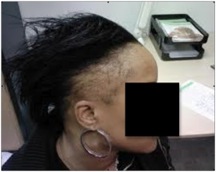

Permanent Hair Loss
- Trichotillomania
- Traction/scarring alopecia
- Alopecia areata, totalis, universalis
- Lupus
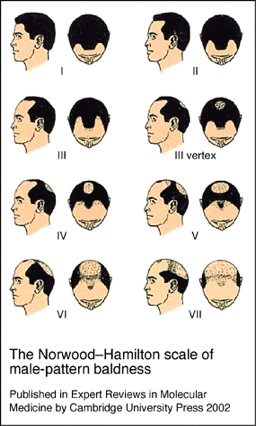
MALE PATTERN BALDNESS
This is a permanent genetic condition that gets carried down from parent to offspring through the X chromosome. Men typically have a warning as to the fate of their hair by looking back at their ancestry, though a family history or lack thereof does not guarantee or negate the condition. The mechanism for MPB starts when testosterone mixes with the enzyme 5-alph-reductase to make dihydrotestosterone, or DHT. While DHT is a hormone present in every human scalp, it is those with genetically weak androgen receptors who suffer hair loss; DHT miniaturizes the susceptible follicles until they virtually disappear. Male pattern baldness shows up through hairline and temple point recession and through thinning at the vertex of the scalp.
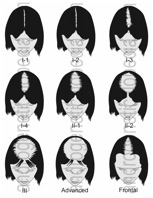
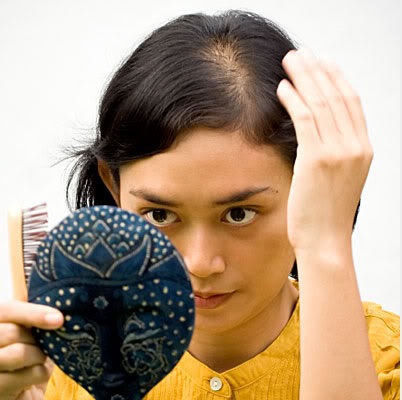
FEMALE PATTERN BALDNESS
Androgenic alopecia in women is also permanent, but has far less to do with genetics and much more to do with aging and hormonal changes. While the family association is not as strong, the mechanism remains the same. Baldness occurs at the work of the hormone DHT, which miniaturizes the follicles with weak androgen receptors. FPB shows up as an evenly spread thinning across the top of the scalp.

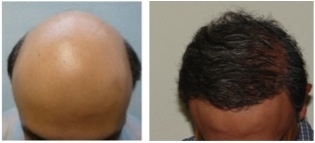
SOLUTIONS
Solutions to hair loss may range from simple dietary adjustments to surgery. Somewhere in the middle lie nutritional supplements, psychiatric treatment, and pharmaceuticals. The solution, of course, is dependent upon the cause. The following may be used to stop different types of hair loss, namely pattern baldness:
- Rogaine (minoxidil)
- Propecia (finasteride)
- Hair transplantation
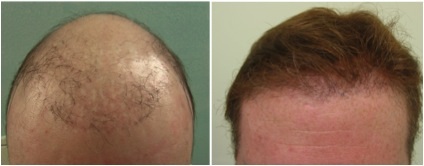
Baldness is often related to genetics. Therefore it is important to consider the patterns that are particular to different ethnic groups. For more information, click here.

